In this information-rich world, information is getting increasingly portable
nowadays. With the huge
demand to deliver global information in a timely and efficient manner, information
sharing needs a
portable platform for real-time response. Portable Electronic Devices (PEDs)
including mobile phones,
laptops, tablets and wearable electronic devices are the most promising ways that
have facilitated the
rapid growth of information sharing and processing.
The heart of these PEDs is their battery chargers, these battery chargers are simply
AC to DC power
converters also known as AC to DC adapters. Since, different PEDs require different
voltage and power
levels to charge their batteries, each PED needs a battery charger of its own kind.
Also, various electronic
devices like digital cameras, speakers, monitors, etc. need dedicated AC to DC
adapters, which can meet
their voltage and power specifications. In summary, the increasing numbers of PEDs
and other electronic
devices result in the manufacturing of a large number of AC to DC adapters and when
discarded, flooding
the earth with an enormous amount of electronic waste (e-waste).
E-waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams, and its disposal is a challenge
for the whole world.
It is estimated that 50 million tons of e-waste have been generated globally in
2018, and half of this
comprises of personal devices such as computers, laptops, smart phones, tablets and
TVs. The discarded
AC to DC adapters of these devices are also contributing to the global e-waste
generation significantly. So,
it is worthwhile to explore the concept of a universal USB charger (single USB
charger for all PEDs), as it
could be a step towards significant reduction of global e-waste generation.
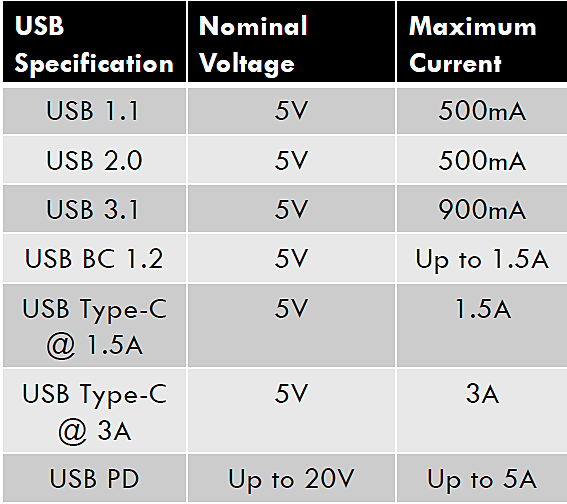
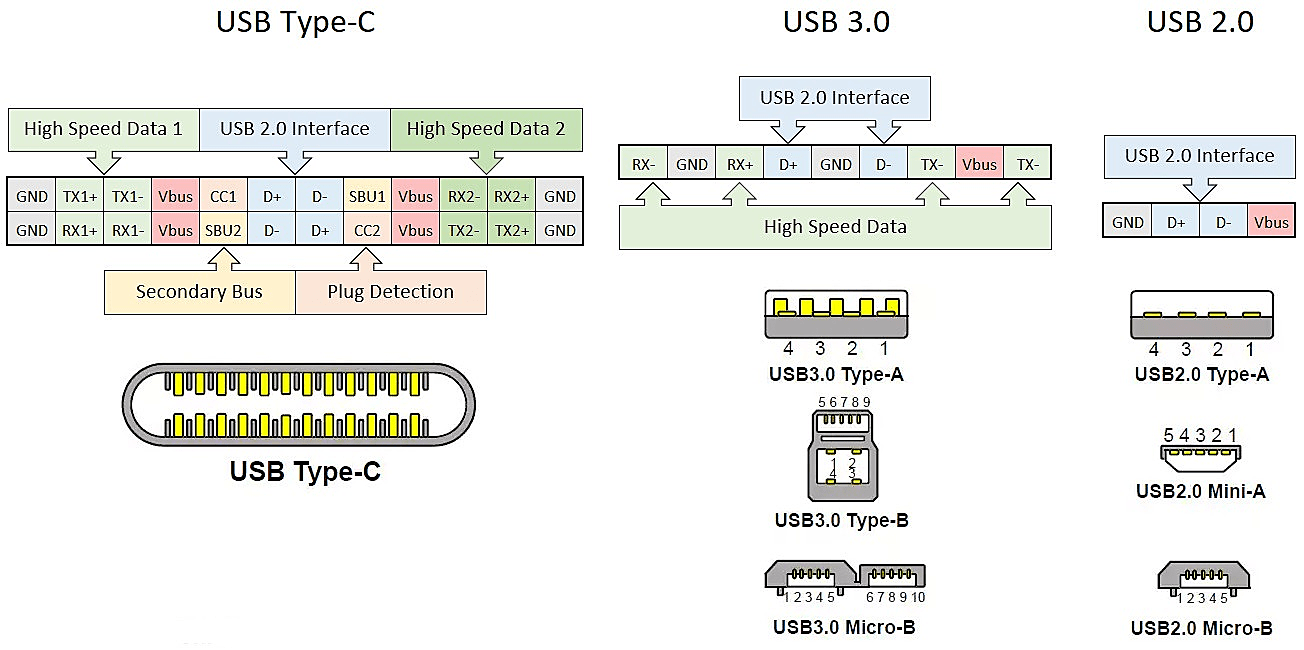
A USB specification is a set of protocols that defines both the data transfer rate and power transfer capability through a USB connector and port. Table below illustrates the evolution of USB specification in terms of their power handling capacity. The first version of USB specification, called USB 1.1, was brought into existence in the 1990s. USB 1.1 specification had a maximum transfer rate of 12 megabits per second (12Mbps) and maximum bus power transfer capability of 2.5 W (5 V, 500 mA).