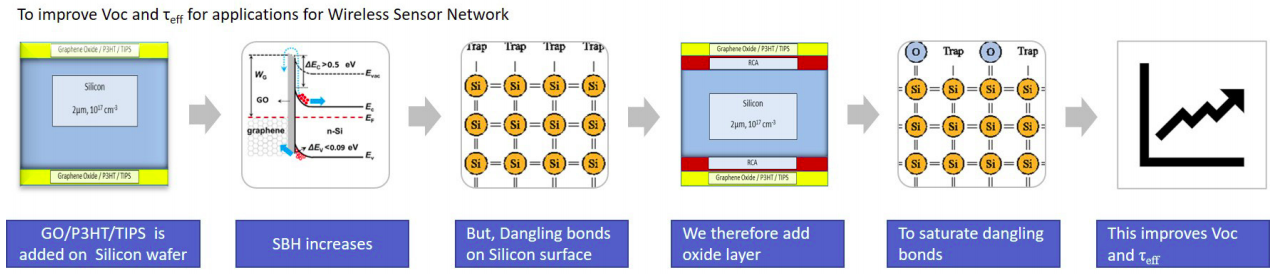
In wireless sensor network (WSN), energy conservation is the biggest challenge. Energy harvesting is at the core of energy conservation and this is where Solar cell becomes the most preferred option. Applications in WSN requires solar cells to be highly efficient with smaller dimensions and easy on budget. Graphene promises to be an effective solar cell material addressing both these requirements. Metal-Insulator Semiconductor structure of Graphene-Silicon solar cells shows enhanced efficiency over Schotttky Junction solar cells. However, small size solar cell using Graphene as one of the electrodes is not providing higher power conversion efficiency. This is where interface tailoring provides us with more avenues to improve efficiency.
To further boost the efficiency, Graphene Oxide (GO) could be the panacea on the
required criteria.
Also, inclusion of RCA Oxide layer between Silicon and the electron blocking layer,
attributes to the
dangling bond saturation which results in reduced interface defects.
To further improve efficiency P3HT and TIPS Pentacene were investigated. A
simulation model was
developed to investigate their passivation abilities. It was clear that, TIPS
pentacene gives better
passivation of Silicon surface. The average open circuit voltage (Voc) of the MIS
silicon solar cell with
TIPS pentacene is higher than that with P3HT and GO. The minority carrier lifetime
also enhances.
Dangling bonds that were present at the silicon surface were an impediment to
improving efficiency
to a higher level. Modifying Silicon surface with RCA oxide address this issue. The
interfacial layer
with a combination of GO + RCA, P3HT + RCA and TIPS pentacene + RCA modifies the Si
surface for
better passivation. The optimum thickness of the interfacial layer, provides
enhanced Voc and
minority carrier lifetime.
The work can be extended by adding Graphene layer with optimum doping and
antireflection
coating to further boost PCE. These solar cells provide the advantage of low cost,
ambient
temperature fabrication process, and hence are more appealing for large scale
production. On the
lines of introducing new interfacial layers, the future work can explore introducing
newer materials.
A slightly different scope can also be explored by considering different solar cell
structures beyond
the one considered here namely MIS solar cell.