

DC distribution is gaining attention due to its energy efficiency, high reliability
and flexibility in connecting
renewable distribution generation. With the emerging distributed energy resources
and semiconductor
technologies, DC distribution is selected for the applications such as low voltage
micro grid, datacenters,
naval ships, etc. The major concern while deploying DC grid is the design of
protection under various fault
ions. Unlike AC systems, there is absence of natural current zero crossing during
breaker operations
in DC systems. Also, fault propagates faster in the DC system, so the protection
device should be really fast.
The circuit breakers that can be used for
protecting DC systems are as follows:
1. Electromechanical circuit breaker: These are traditionally used in AC system. That can also be used for DC system after de-rating. It clears the fault in 2 to 3 cycles i.e. 60 msec.
2. Hybrid circuit breaker: Hybrid circuit: Hybrid circuit breakers are used for both AC and DC system protection. It is, basically, an integration of both electromechanical and solid state circuit breaker. Its fault clearance time is around 2 msec to 30 msec and current commutation process is really complex.
3. Solid state circuit breaker: It uses the semiconductor device as the main
switch, hence known as
solid state circuit breaker. Its fault clearance time is less than 1 msec, which is
faster than any other breaker.
Solid state circuit breakers commonly employ fully controlled device such as IGBT,
as a main line switch.
Hence, the occurrence of fault needs to be sensed and turn off command is to be
provided to the switch
using an external control unit, in order to clear the fault. However, use of sensors
and external control unit
makes system more complex.
Z-source circuit breaker is a type of solid state circuit breaker which uses SCR as
the current breaking
element. SCR turns ON when triggered through gate pulses and it turns OFF when the
current through it
falls below its holding current. Thus, no turn off command is required for SCR
commutation. The Z-source
breaker topologies make use of passive elements to achieve current zero crossing in
power line, which
assists the commutation of SCR. Therefore, Z-source circuit breaker can isolate
fault without use of any
sensing circuitry, unlike other solid state CBs and is capable of isolating the
fault in tens of microseconds.
Z-source circuit breaker can be used to protect DC systems such as micro grid, data
centers, EV battery
system and naval ships. In such applications, power flows in both directions. These
systems require circuit
breakers which are capable of isolating the fault during either direction of power
flow. Bi-directional
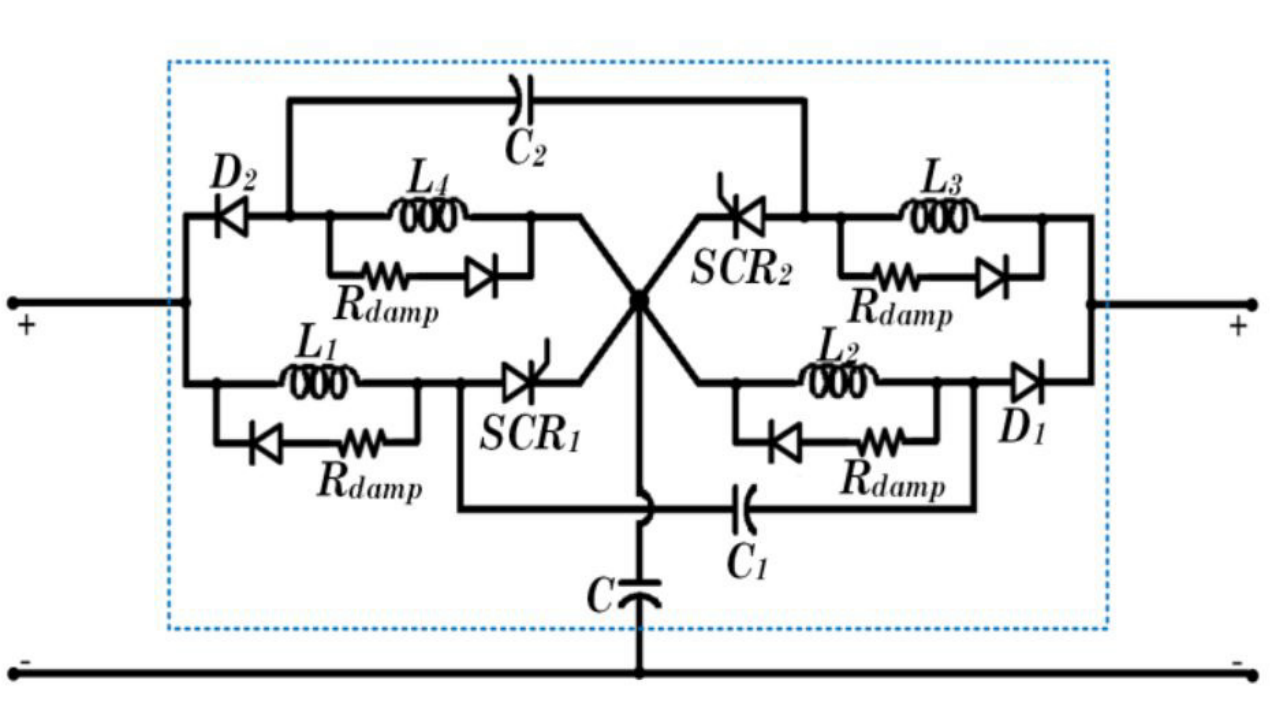
Z-source breaker (Bi-ZSB) as shown in figure is designed and developed for similar
applications. For forward
direction of power flow, combination of inductors (L1
& L2
) and capacitors (C1 & C) are utilized to turn off
SCR1 during fault ion. Similarly, for reverse direction of power flow, combination
of inductors
(L3
& L4
) and capacitors (C2
& C) are utilized to turn off SCR2 during fault ion. The novel circuit breaker
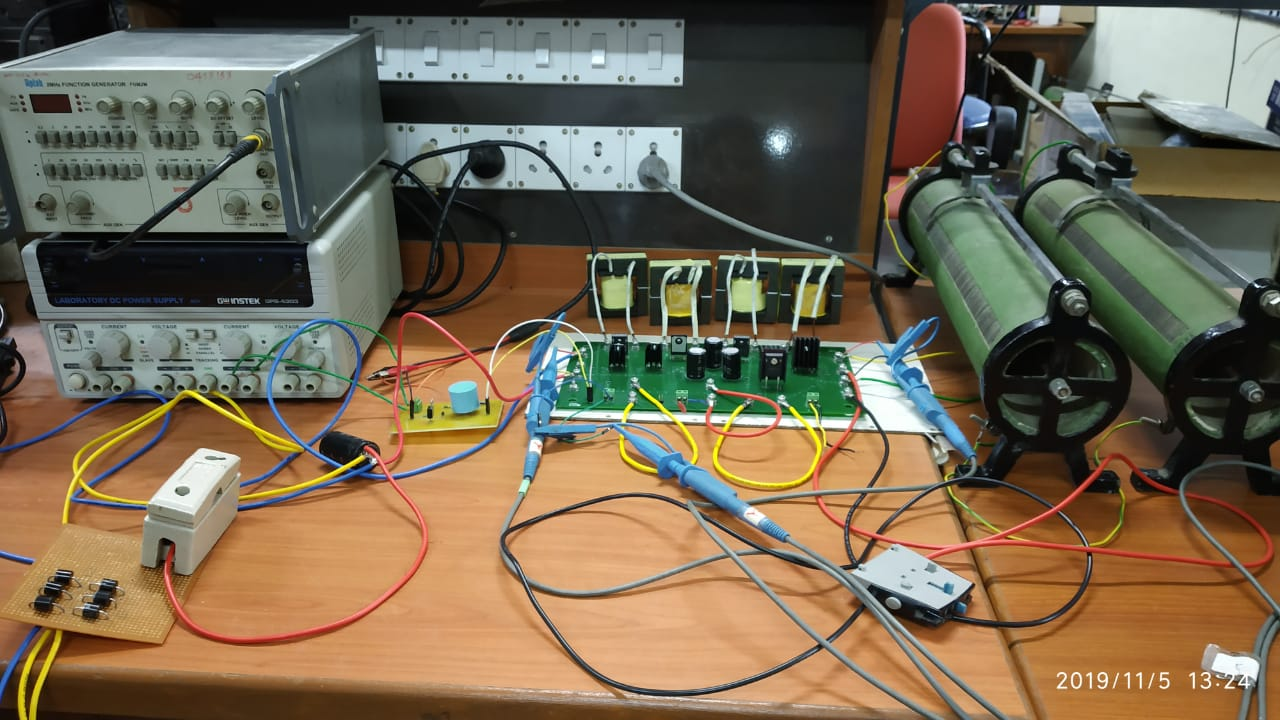
is designed and developed for 380V, 16A. It isolates the fault within 300
microseconds.



